Finite-state machine design, with th eurpose of returning minimum change, was used to create a virtual vending machine. The vending machine simulates drink selection & payment via keyboard entries.
Source Code can be found here: https://bitbucket.org/nicho755/me-305-labs/src/master/ME405_Lab0x01_Vendotron/ME405_Lab0x01.py
The vending machine has four input buttons representing four different beverages that users can select from with corresponding prices: 1) Cuke = $1.00 2) Popsi = $1.20 3) Spryte = $0.85 4) Dr. Pupper = $1.10
In addition, the machine take in user input in the form of money being inserted through the "Insert Coin" slot and requesting for the current balance to be returned via the eject button. The machine will output strings on the LCD screen and display current balance, insufficient funds, drink output confirmation, and amount of change returned.
To ensure the machine runs like a finite state machine, the script cannot include any blocking, or input, commands, the program must account for the following behavior:
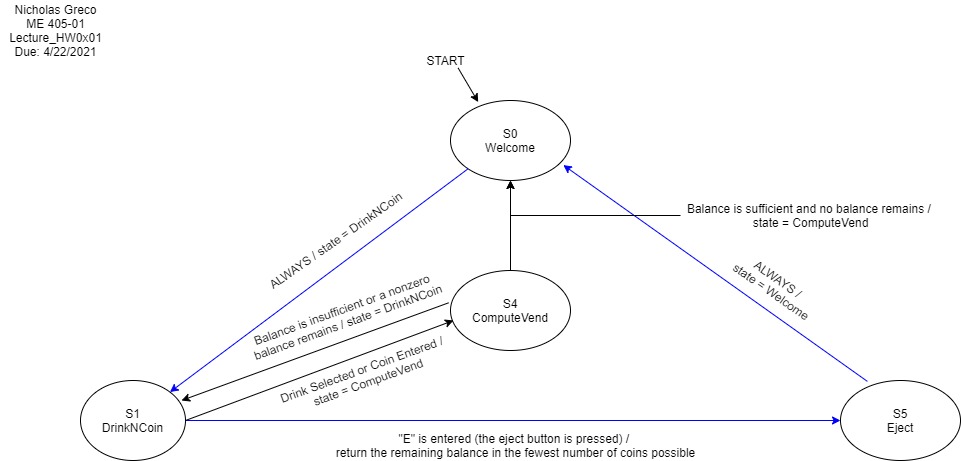
Below is the finite state machine diagram for the vending machine. (Adapted from my HW 0x00 submission)
Users are able to input the following valid commands via keyboard
Payment Input
'0' - insert 1 cent
'1' - insert 5 cents
'2' - insert 10 cents
'3' - insert 25 cents
'4' - insert 1 dollar
'5' - insert 5 dollars
'6' - insert 10 dollars
'7' - insert 20 dollars
Selecting Drink:
'C' or 'c' - select Cuke
'P' or 'p' - select Popsi
'S' or 's' - select Spryte
'D' or 'd' - select Dr. Pupper
Return Balance
'E' or 'e' - eject change